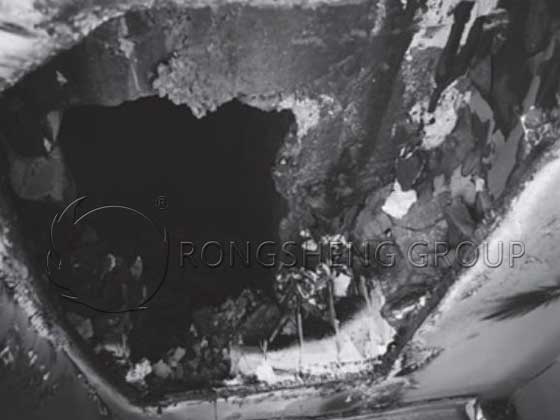
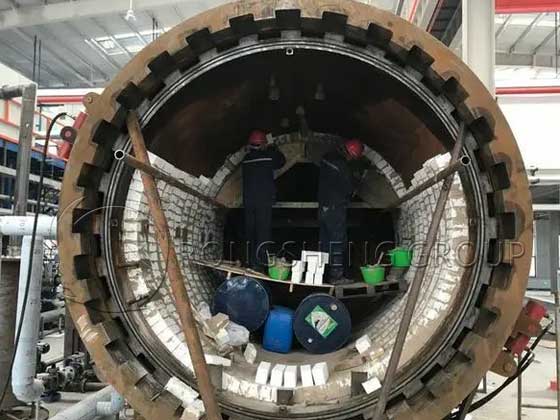
The magnesia refractory bricks used in the burners of general sleeve lime kilns are prone to breakage within more than one year of use. This makes the service life of the burner bricks inconsistent with the life of the kiln body. One-third of the burner bricks of the sleeve lime kiln broke within less than one year of use, while the service life of the lime kiln is more than 3 years. Therefore, the service life of the burner bricks is inconsistent with the life of the kiln body. Although the breakage of the burner bricks does not affect the use of the lime kiln, it has a certain negative impact on the calcination process.
The Reason Why Burner Bricks are Easy to Break
The reason why burner bricks are easy to break is that the material used for burner bricks is magnesia refractory bricks. In addition to having excellent high temperature resistance and anti-lime reactivity, this alkaline material has the following unfavorable factors, which lead to premature breakage.
- 1: Magnesium refractory materials have large thermal expansion and poor thermal shock resistance. The burner bricks are washed by the hot air flow of the flame, and the thermal shock environment they endure is harsh, which makes them prone to cracks caused by thermal shock.
- 2: Due to the large thermal expansion coefficient, the thermal stress of magnesium refractory materials is high. When there is local stress concentration, it is easy to break.
- 3: Magnesium refractory materials are easy to hydrate, resulting in bulging and cracking. They are greatly affected by environmental conditions during construction. Improper baking is also prone to cracking, resulting in falling blocks. In cold and humid weather, the moisture in the fire mud is not easy to remove, and it is easier for the bricks to hydrate. Therefore, the construction environment conditions and baking requirements are strict
- 4: Magnesium refractory materials have low hot strength and are prone to creep under thermal stress.
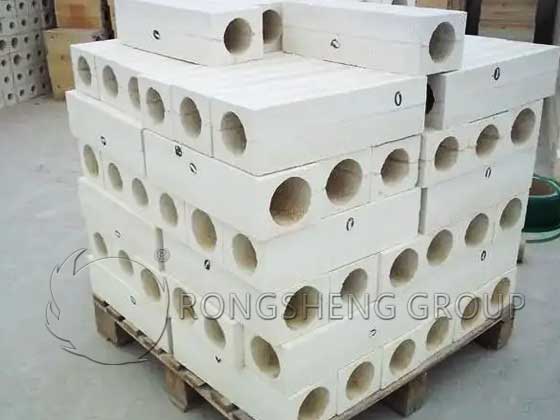

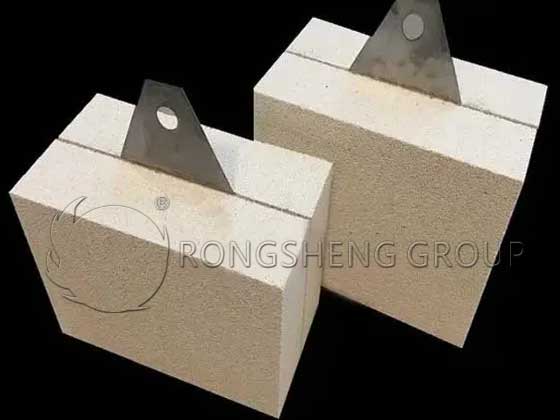
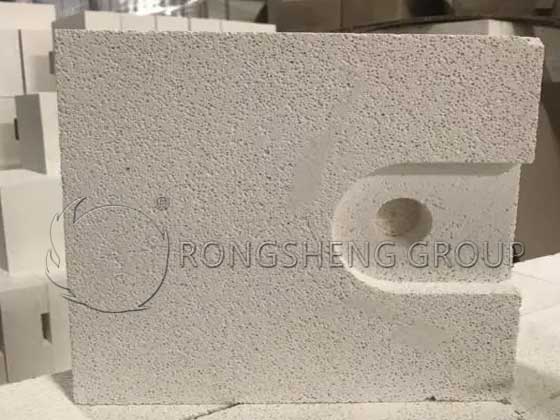
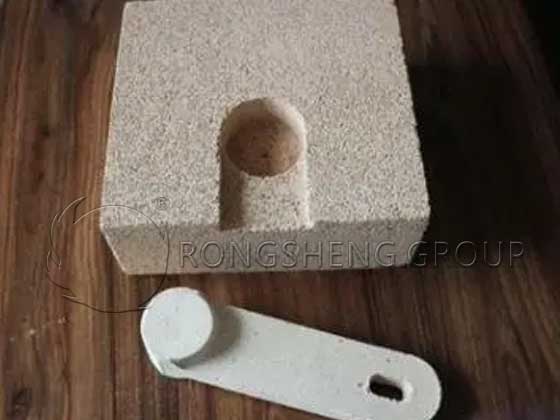
Corundum-Mullite Burner Brick
Improvement of burner brick material The choice of corundum-mullite refractory castables to make burner brick prefabricated parts has the following advantages:
- 1: The main crystal phases of corundum-mullite refractory castables are corundum and mullite. The former has a high melting point of 2050℃, hardness and strength, can resist high temperature and airflow erosion, and has excellent high temperature wear resistance. The melting point of mullite is also relatively high at 1840℃, and its characteristic is a small thermal expansion coefficient. The crystal has a needle-column mosaic structure and has good thermal shock resistance. The composite refractory castable of corundum phase and mullite phase has the advantages of both, which can effectively resist the erosion of burner bricks by flame hot air flow. It can withstand harsh thermal shock environments and prevent burner bricks from breaking.
- 2: There is no hydration problem with corundum mullite refractory castables, and the construction is less affected by the environment. The construction conditions are not demanding, and the pouring, curing and heat treatment can be carried out at the material supplier, so the quality is easy to be guaranteed. It will not hydrate and crack during construction and baking.
- 3: The burner brick is a special-shaped brick, which is not easy to be machine-pressed. The pouring method is easy to achieve integral or split forming, and realize precise control of shape and size. The critical particle size of machine-pressed bricks is limited, generally 5 mm, while the critical particle size of castables can be as large as about 20 mm, which is conducive to the stability of the structure and improves the resistance to thermal shock.
- 4: When the burner brick is in use, the gas (or fuel oil) is sprayed into the furnace, and the CaO dust in the furnace is not easy to adhere to the burner cavity, and the reaction of CaO and Al2O3-SiO2 materials will not occur. Even if a small amount of CaO adheres to the burner brick, the Al2O3 content in the burner brick is high (greater than 75%), while the content of SiO2 and CaO is relatively low. According to the A12O3-SiO2-CaO ternary phase diagram, the temperature of the reaction is about 1500℃. It can be considered that the solid phase reaction of Al2O3-SiO2-CaO is not easy to occur at the working temperature of the lime kiln.
The magnesia refractory bricks used in the burners of general sleeve lime kilns are prone to fracture after more than a year of use, which makes the service life of the burner bricks out of sync with the life of the kiln body. That is, the burner of the sleeve kiln is prone to fracture. By analyzing the cause and reproducing the prefabricated burner bricks made of corundum mullite refractory castables suitable for the burner of the sleeve kiln according to the combustion process of the lime kiln calcining zone and the structure of the lining refractory material, the problem of burner brick fracture is effectively solved. And practice shows that the service life of the corundum mullite burner bricks is synchronized with the life of the kiln body.
Performance of High-Purity Mullite Refractory Bricks for Lime Kilns
High-purity mullite refractory bricks for lime kilns have important application value in the field of refractory materials. High-purity mullite refractory bricks for lime kilns are a type of refractory material specifically used in the lime kiln industry. It is made of high-purity mullite as the main raw material and sintered at high temperature. High-purity mullite refractory bricks for lime kilns have good wear resistance, high temperature resistance, shock resistance and corrosion resistance, and are an indispensable and important material in lime kiln production.
- First of all, lime kiln high purity mullite refractory bricks have excellent refractory performance. This refractory performance advantage ensures the reliability of lime kiln high purity mullite refractory bricks during long-term use.
- Secondly, lime kiln high purity mullite refractory bricks have excellent wear resistance. High purity mullite refractory bricks have high hardness and wear resistance, which can effectively resist the wear of materials and extend service life.
- Next, lime kiln high purity mullite refractory bricks also have good seismic resistance. Lime kiln high purity mullite refractory bricks have good seismic resistance, which can effectively resist the influence of vibration on its structure and performance, and ensure long-term stable operation of equipment.
- In addition, lime kiln high purity mullite refractory bricks also have good corrosion resistance. Lime kiln high purity mullite refractory bricks can resist the erosion of chemical substances and maintain their stable performance.
In short, lime kiln high purity mullite refractory bricks have excellent refractory performance, wear resistance, seismic resistance and corrosion resistance. Suitable for the production environment of various types of lime kilns. Its application can improve the working efficiency of the lime kiln, extend the life of the equipment, and reduce production costs. It is an indispensable and important material in the lime kiln industry.